Across every sector, organizations handle an overwhelming volume of documents, PDFs, invoices, contracts, receipts, forms, shipping documents, and much more. Manually pulling out information and keying it into systems slows operations, consumes resources, and often leads to mistakes that could easily be avoided.
That’s where MuleSoft’s Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) truly makes an impact. IDP helps cut down manual work and enables companies to automate document-heavy workflows with far greater efficiency and ease.
In this blog, lets understand how to configure, train and test IDP on MuleSoft Anypoint platform.
What is MuleSoft IDP?
MuleSoft Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) is a capability within MuleSoft that automatically extracts, interprets, and structures data from unstructured documents, like invoices, purchase orders, receipts, forms, letters, and PDFs.
Instead of humans reading documents and manually entering data, MuleSoft IDP uses AI + OCR + MuleSoft integration to understand the content and push clean, structured data into downstream systems such as Salesforce, ERP, databases, or APIs.
What MuleSoft IDP Does
It helps you:
- Read documents (PDFs, images, scans, handwritten or typed)
- Extract key fields (amount, date, PO number, vendor name, etc.)
- Classify the document type (invoice, contract, PO, form, etc.)
- Validate data (business rules, formats, reference data)
- Integrate the results into your business systems using MuleSoft APIs
How It Works
- Upload or receive a document
- via API, email, SFTP, app, or a form.
- IDP extracts information
- using OCR + AI models.
- The extracted fields are validated
- using business rules in MuleSoft.
- Data is sent to target systems
- (Salesforce, SAP, databases, etc.) using APIs.
- Human review (optional)
- for low‑confidence fields.
What is required to use MuleSoft IDP
- Access to Anypoint Platform
- You must have a MuleSoft account with access to the IDP capability and document action editor.
- Automation Credits
- IDP document processing consumes Automation Credits, so your MuleSoft subscription must include them.
- User Permissions
- to create and execute the document actions on Anypoint Platform
User Permissions Required
Users with Administrator privileges inherently possess all required permissions and do not require additional access. Users without Administrator privileges must obtain the necessary Document Action permissions.
The following three permissions are required for the user who wants to create and configure document actions on Anypoint platform
- Manage Actions
- Build Actions
- Execute Published Actions

Once access is granted user will be able to see the MuleSoft IDP dashboard, where he can create, configure the document actions, and can review the documents that did not meet the desired confidence level threshold during automation. Once completed, he can Publish document actions seamlessly in RPA and Exchange.

High Level Steps in Using the Document Actions
- Identify the type of document to process.
- Like is it a Purchase Order, Invoice, Time Sheet or image etc etc
- Identify the fields of Interest in the document.
- Like what in the document we need to extract and put it in a structured format
- Create document action.
- Like giving a unique name to the document action, create and configure the action
- Train the model
- Like experimenting with a range of sample documents so that the underlying AI model can learn what to extract given unstructured data formats in the document,
- Add reviewers.
- Mark users who would review the documents that could not pass thru automation, where the model is not confident if it was able to fetch desired data from the document being injected
- Publish the document action to Anypoint exchange and or to MuleSoft RPA
- Making it document action taking a REST API route so that consumer applications and APIs can start interacting with the automation
- Test the asset
- Verify access control, availability and completeness of the document action thru postman or other rest clients to isolate and fix any issues or improvise the document action
Step # 1: Identify document type
In our usecase, we are using a purchase order as the type of the document to exhibit the automation, below is a Purchase Order sample being used in this article.

here is the sample architectural flow we are using in this article. Incoming Email will be treated as the triggering point for the automation
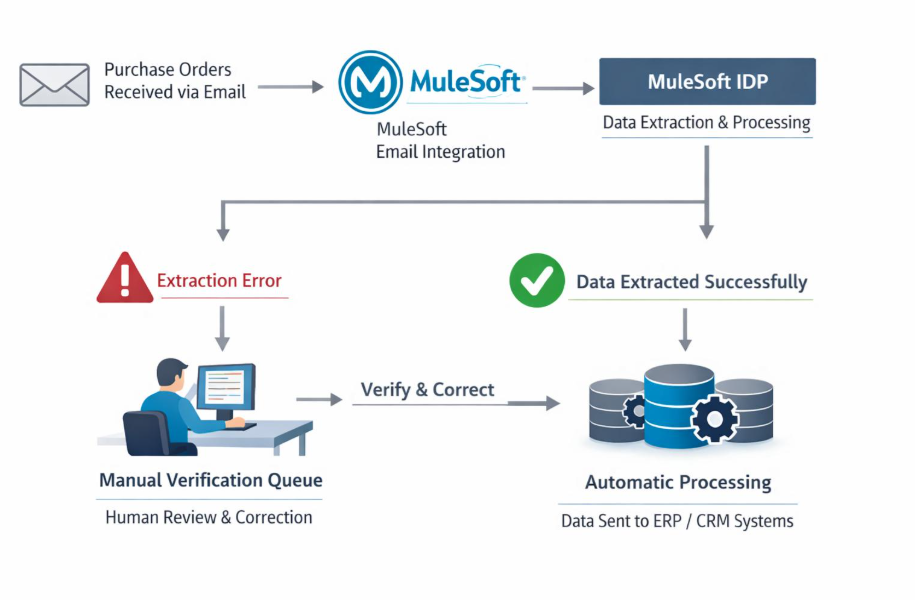
Step # 2: Identify the fields of Interest in the document.
From the given document template, we shall be interested in extracting the buyer abd seller names, contact numbers, line items details and pricing details, so we shall be creating a mapping of such fields
| S.No. | Desired Field | Mapped field in the document | Remarks |
| 1 | Purchase Order Number | PO Number | |
| 2 | Seller | Vendor details | |
| 3 | Buyer Details | Ship to | |
| 4 | Item | Item | |
| 5 | Quantity | QTY |
Step # 3: Create document action
A document action in MuleSoft IDP is an AI-powered process that reads a document, extracts the important fields, removes unwanted data, and returns a structured JSON output. IDP provides ready-made Invoice and Purchase Order templates with predefined fields, making setup quick and accurate. We just pick the template that matches our document type.
If document doesn’t fit these categories, IDP’s Generic template gives full flexibility. We can describe the fields we want in natural language, allowing us to customize extraction easily for any unique document format.
To complete the Document Action setup, select the appropriate document type, provide a meaningful name and description, and then continue.
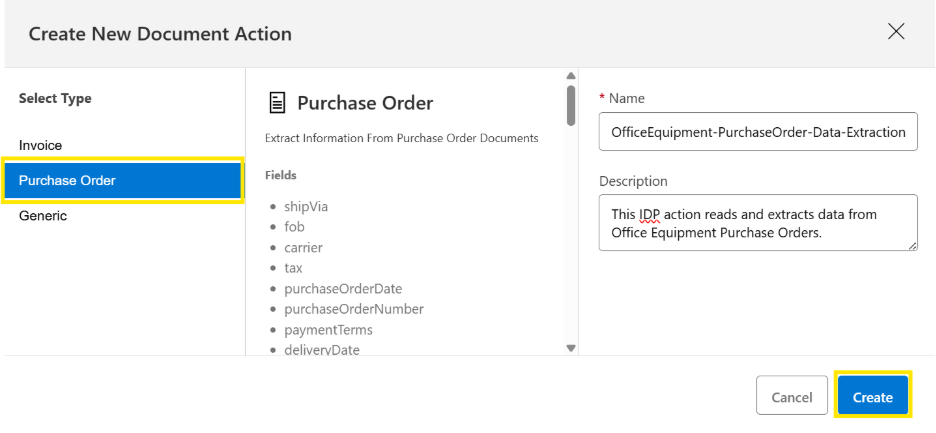
After creating a document action, we need to configure two key settings:
1. Mark Required Fields
Choose the fields that must always be extracted.
If a required field is missing, the document is automatically sent to the review workflow for manual validation ( If configured ).
2. Set Confidence Thresholds
Define the minimum confidence level for each field.
If the extraction confidence is lower than the defined threshold, the field (or document) will be sent for review to ensure accuracy.
These settings help ensure that important data is always captured correctly, and any uncertain or incomplete extraction is flagged for human review.

Step # 4: Train the model
IDP enables the configuration of custom prompts for individual document actions. Once document parsing is complete, the responses to these prompts are included in the structured output. Using an internal NLP model, IDP can interpret natural-language queries and extract the requested information.
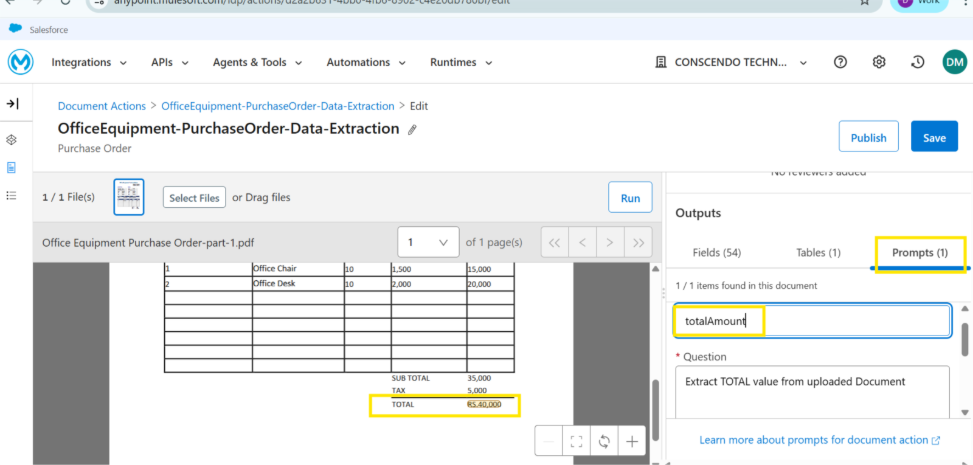
Once training is completed by configuring the prebuid fields and custom field configuration by providing prompts for required data, we can run Document Action. During this process, IDP internally scans the uploaded document and analyzes its content using an NLP-based extraction engine. The system then extracts the configured field values and returns them along with corresponding confidence scores, indicating the accuracy and reliability of each extracted value.

Step # 5: Add reviewers
If the confidence score of the extracted data falls below the expected threshold, the extracted data requires human intervention. The document is routed for manual review, where a designated reviewer verifies and corrects the extracted values as needed. To enable this review workflow, a reviewer must be configured in the system settings as part of the document configuration.


Step # 6: Publish the document action to Anypoint exchange or MuleSoft RPA
After completing the IDP configuration and adding the required reviewers, the Document Action must be saved and published to the Exchange. Upon the first publication, the Document Action is assigned to version 1.0.0. With every subsequent update to the IDP configuration, a new version is generated each time the changes are saved and published, ensuring proper version control and traceability.
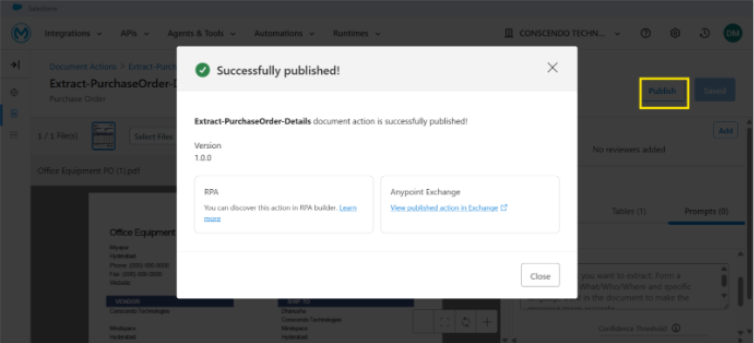
Once the Document Action is published to the Exchange, the system exposes APIs that can be used to extract data from documents. These APIs can be consumed within Mule integrations or integrated with other downstream systems and services to automate document processing and data flow across the enterprise.

Step # 7: Test Published IDP APIs
After publishing the Document Action to the Exchange, the system provides REST API endpoints, including POST and GET operations. The POST endpoint is used to submit a document to the Document Action for processing. Upon successful submission, the API returns an execution ID, which is required to track the processing status and retrieve the extracted data.
To test the API using Postman, follow the sequence below
- Obtain the access token.
- Submit the document to the Document Action using the POST API.
- Retrieve the document data using the GET API.
Obtain the access token:
To obtain access to the APIs, secure credentials are required. For this purpose, a Connected App must be created in Access Management, which provides the Client ID and Client Secret. These credentials are used to request an OAuth access token, enabling secure authentication and authorization for API calls. The OAuth token endpoint URL can be obtained from Anypoint Exchange, where the published API details are available.
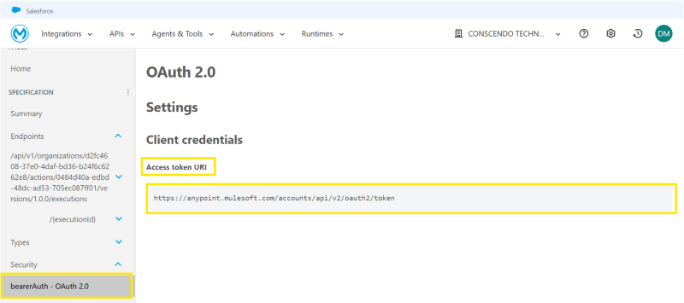
Below is the screenshot of the postman to obtain the access token

Submit the document to the Document Action using the POST API:
After obtaining the access token, the document is submitted to the Document Action using a POST request as form-data. This request initiates the document processing and data extraction workflow. Upon successful submission, the API returns an execution ID, which uniquely identifies the processing instance and is used to track the execution status and retrieve the extracted results.
Below is the curl command for the POST method
curl –location ‘https://idp-rt.{region}.anypoint.mulesoft.com/api/v1/organizations/{orgId}/actions/{actionId}/versions/{actionVersion}/executions’ \
–header ‘Authorization: Bearer {token}’ \
–form ‘file=@”{pathToFile}”‘
Find the below screenshot for the postman for POST call.

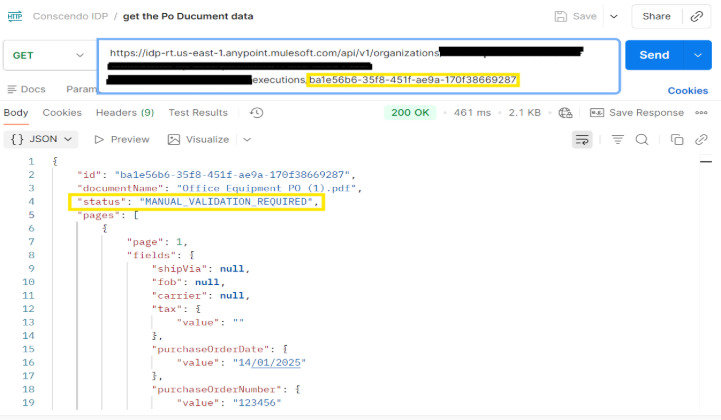
Retrieve the document data using the GET API:
Once the document is posted, the Document Action begins processing, which may take some time depending on the document size and complexity. The execution ID returned from the POST request should be used as a URI parameter in the GET request to track the status of the processing.
If the GET endpoint is called while the extraction is still in progress, the response will indicate the status as “IN_PROGRESS”. Once the extraction is complete, invoking the GET endpoint with the execution ID returns the fully extracted and structured data in JSON format, including all configured field values and their details.
In addition to “IN_PROGRESS”, the API may return other status values such as:
- ACKNOWLEDGED – The document has been received and queued for processing.
- RESULTS_PENDING – Processing is complete, but the results are not yet finalized.
- MANUAL_VALIDATION_REQUIRED – Human intervention is needed to review or correct extracted data.
- FAILED – Processing failed and no data was extracted.
- PARTIAL_SUCCESS – Some fields were extracted successfully, but others may require review.
- SUCCEEDED – Extraction completed successfully, and the data is ready for further processing.
Based on the returned status, appropriate actions can be taken to either continue automated workflows or route the document for manual review before further processing.
Below is the curl command for the get method
curl –location \
‘https://idp-rt.{{region}}.anypoint.mulesoft.com/api/v1/organizations/{orgId}/actions/{actionId}/versions/{actionVersion}/executions/{executionId}/v2’ \
–header ‘Authorization: Bearer {token}’
Please find the screenshot of postman for the GET method
Conclusion
In this blog, we covered the complete setup of MuleSoft Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)—from identifying document types and fields to configuring, training, and reviewing extracted data. We also explained how to publish the IDP API to Anypoint Exchange and validate it using Postman. This end-to-end approach helps streamline and automate document processing.
We hope this information supports you in your IDP learning journey.
For more insights on IDP such as the
-Lifecycle of MuleSoft Intelligent Document Processing
-Steps involved in architecting an IDP solution in MuleSoft
-MuleSoft IDP production lessons learned, common mistakes, and what we would do differently.
For more blogs on MuleSoft IDP, refer to https://conscendo.io/category/intelligent-document-processing/


